AbstractPurposeThis study aimed to evaluate the technical feasibility, efficacy, and safety of anterolateral hydrodissection (ALHD) in radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for benign thyroid nodules.
MethodsBetween November 2019 and April 2020, 39 patients underwent 41 sessions of RFA with the ALHD technique to treat benign thyroid nodules. ALHD was performed with cold (0°C-4°C) 5% dextrose solution during RFA to minimize pain and secure sufficient safety margins from critical neck structures. The initial ablation ratio (IAR) was measured to assess the technique’s efficiency. Ultrasound examinations, symptoms, and cosmetic scores were evaluated pre-procedure and at 6 and 12 months post-procedure. Procedure-related pain during RFA and complications were recorded.
ResultsThe mean index nodule volume was 20.5±21.6 mL. ALHD was technically feasible in all patients. The mean IAR was 90.7%±8.3%, and significant reductions in mean nodule volume were noted at 6- and 12-month follow-ups (P<0.001, 63.9%±19.0%, and 76.3%±18.9%, respectively). Symptom and cosmetic scores showed significant improvements at 6- and 12-month follow-ups (P<0.001). Pain during the procedure was well-controlled with ALHD in all patients. After the initial use of 5-10 mL of lidocaine at the start of the procedure, no further lidocaine injection was given to any patient. Transient voice change was observed in one patient, but the patient recovered spontaneously within 30 minutes.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is used to treat benign thyroid nodules and thyroid cancers, and many studies have demonstrated its efficacy and safety [1,2]. However, several long-term follow-up studies have reported a tendency for marginal regrowth after 2 to 3 years of follow-up [3-5]. Therefore, repeated RFA is often required for nodules showing marginal regrowth [3]. To prevent marginal regrowth, it is crucial to achieve complete ablation of the nodule, including the margins, while minimizing the amount of residual tissue [6,7]. To achieve more complete ablation, two types of vascular ablation techniques have been proposed: the artery-first ablation technique and the marginal venous ablation technique [8,9].
Of these two vascular ablation techniques, the venous ablation technique directly ablates the marginal draining veins. Ablation of these marginal draining veins is useful for complete ablation of the nodule margin, thereby preventing marginal regrowth [3,9]. However, it is technically difficult to ablate the margin of the nodule completely because of pain. In addition, there is a greater risk of complications when the nodule tissue is close to a critical structure, such as medial type vagus nerves and medial type sympathetic ganglia, as well as in cases of anatomic variations of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. To overcome these difficulties, it is helpful to use the hydrodissection technique with 5% cold dextrose solution [10,11].
The hydrodissection technique involves creating a sufficient safety margin by injecting a solution around the thyroid capsule to separate the target ablation area from adjacent critical structures. Various hydrodissection techniques and four different approaches can be used (the anterolateral, posterior, pre-tracheal, and danger triangle approaches), with the choice depending on the tumor location [12]. For several years, the thyroid ablation team at the authors’ affiliated institution has routinely used the anterolateral hydrodissection (ALHD) technique to safely facilitate venous ablation and prevent marginal regrowth of benign thyroid nodules. This study presents the authors’ experience of ALHD for the ablation of benign thyroid nodules, introducing the preliminary cases using the ALHD technique and evaluating its technical feasibility, efficacy, and safety during RFA of benign thyroid nodules.
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board (2021-1452) of Asan Medical Center. The requirement for written informed patient consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of the study.
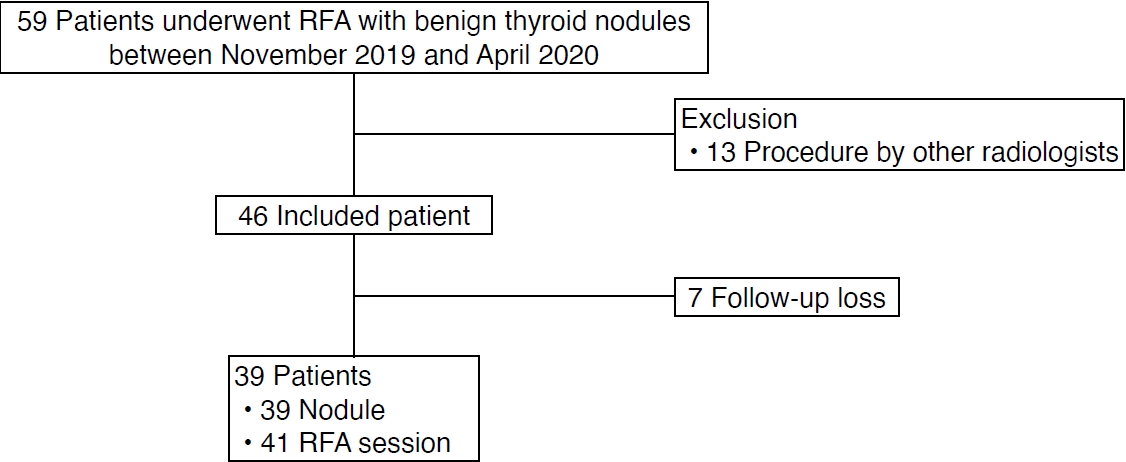
Between November 2019 and April 2020, 59 patients underwent RFA for biopsy-proven benign thyroid nodules causing cosmetic or symptomatic problems (Fig. 1). Thirteen patients who were treated with RFA by radiologists other than J.H.B. were excluded. Seven patients who were lost to follow-up before 6 months were also excluded. Finally, 39 patients with 39 benign thyroid nodules who underwent a total of 41 RFA sessions were included in this study. All procedures in the included cases were performed by an experienced radiologist (J.H.B. with 26 years of clinical experience in performing the procedure).
Ultrasound examinations were performed using ATL HDI 5000, iU22 (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands), or RS 80 (Samsung Medison Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea) systems. Each system was equipped with a linear high-frequency probe (5-14 MHz). All ultrasound examinations and ultrasound-guided core needle biopsies were performed under the supervision of staff radiologists with at least 11 years of clinical experience in performing and evaluating thyroid ultrasound images.
Three orthogonal diameters were measured, and the volume of each nodule was calculated. The nodule composition was graded into four categories according to the proportion of the solid component: grade 1, solid with no obvious cystic content; grade 2, predominantly solid with a cystic content ≤50%; grade 3, predominantly cystic with a cystic content >50%; and grade 4, cystic with no obvious solid content [13]. Nodule vascularity was graded into four categories on the basis of a Doppler examination: type 1, no intra-nodular vascularity; type 2, peri-nodular vascularity only; type 3, intra-nodular vascularity <50%; and type 4, intra-nodular vascularity >50% [13].
Before RFA, the physician recorded a cosmetic score as follows: 1, no palpable mass; 2, no cosmetic problem but a palpable mass; 3, cosmetic problem on swallowing only; and 4, readily and always detected cosmetic problem. Baseline patient-determined symptom scores were rated using a visual analogue scale from 0 to 10 [14].
RFA was performed according to the guidelines of the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology [14]. RFA was performed using a radiofrequency generator (VIVA RF generator, STARmed, Goyang, Korea; M-2004, RF Medical, Seoul, Korea) and 18-gauge thyroid-dedicated modified internally-cooled electrodes (VIVA, STARmed; RFT-0710, RF Medical) with various active tip sizes. The size of the active tip (5, 7, and 10 mm) was selected according to the size of the thyroid lesion.
The ALHD technique was routinely used for RFA of benign thyroid nodules. A 21G spinal needle with a three-way stopcock was used for both local anesthesia and ALHD with a single skin puncture site (Fig. 2). The overall procedure of ALHD with RFA is illustrated in Fig. 3. First, for local anesthesia, a lidocaine needle was inserted at the midline of the anterior neck, just above the thyroid isthmus, and advanced into the thyroid capsule. The patient was injected with 1% lidocaine at the skin puncture site and the perithyroidal area including the strap muscle and thyroid capsule. Next, RFA of the benign thyroid nodule was started. RFA was performed using the trans-isthmic approach and the moving-shot technique, and the ALHD technique was routinely applied during the RFA procedure. We approached the target nodule by dividing it into three portions and ablating them in the following order. First, the most anteromedial portion of the nodule near the isthmus was targeted for ablation. Second, the central portion of the nodule was targeted. Lastly, the peripheral portion of the nodule, which was relatively close to critical perithyroidal structures, was targeted with hydrodissection. If the patient complained of pain during ablation of the nodule margin, additional ALHD was performed (instead of using more local anesthesia) with cold (0°C to 4°C) 5% dextrose solution to control the pain and secure sufficient safety margins from critical structures (Fig. 4). Injection of fluid and constant monitoring of the relationships between the nodule and critical structures including nerves, esophagus, and pain-sensitive structures such as the strap muscle and skin were required. The distance between the thyroid gland and strap muscle was maintained at more than 5 mm. RFA was terminated when the entire targeted lesion was covered with hyperechoic microbubbles. The amount of 5% dextrose solution used in ALHD varied according to the size of the index nodule and was usually between 30 and 50 mL.
Procedure-related pain was graded into four categories: grade 0, radiofrequency power did not have to be turned off because the patient experienced no pain; grade 1, radiofrequency power was turned off once or twice to reduce pain levels; grade 2, radiofrequency power was turned off more than three times; and grade 3, the procedure was terminated before completion because of severe pain [15,16]. Complications and side effects were defined according to the quality improvement guidelines of the Society of Interventional Radiology and a prior multicenter evaluation of complications [9,17].
After RFA, the initial ablation ratio (IAR), a semi-quantitative index that measures the amount of ablation, was calculated to predict the efficacy of the technique. The IAR is the ratio of the ablated nodule tissue volume (Va) to the total nodule volume (Vt) immediately after RFA, as expressed in the formula IAR=(Va/Vt)×100 (%). Since the ultrasound image immediately after RFA is often unclear because of hemorrhage and edema, Va and Vt are indirectly measured. Vt is the same value as the index nodule volume measured before RFA, whereas Va is calculated using the viable volume measured on ultrasound imaging taken 1 month after treatment (Vv1mo), where Va=Vt-Vv1mo. Therefore, the following formula was used in this study: IAR=(Vt-Vv1mo)/Vt×100 (%) [4,5,18].
Follow-up ultrasonography (US) was performed at 1, 6, and 12 months after RFA, and changes in nodule size and volume were evaluated. Volume reduction was calculated as follows: volume reduction ratio (VRR, in %)=[(initial volume-final volume)×100]/initial volume. Therapeutic success was defined as a volume reduction >50% of the initial nodule volume on a follow-up US examination [19]. The therapeutic success rate was defined as the percentage of successfully treated nodules [20].
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The long-axis diameter and the calculated volumes of the RFA zones are reported as mean±standard deviation. The diameters and calculated volumes of the ablation zones and ablated nodules obtained at each follow-up examination were compared using the Student t-test. All P-values were two-sided, and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The 39 patients with biopsy-proven benign thyroid nodules underwent a total of 41 RFA sessions. Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the patients and nodules. The mean longest dimension and volume of the index nodules were 4.2±1.4 cm (range, 1.6 to 8.1 cm) and 20.5±21.6 mL (range, 1.0 to 108.5 mL), respectively. The mean total radiofrequency (RF) energy used was 2,296.8±1,906.1 J (range, 519.7 to 11,168.0 J). The treatment characteristics of the 41 RFA sessions are listed in Table 2. More than 30 mL of 5% dextrose solution was used in each case. In all patients, ALHD adequately controlled pain during the procedure. No patient received an additional lidocaine injection after the initial use of 5–10 mL at the start of the procedure.
The mean IAR was 90.7%±8.3% (range, 70% to 100%). Table 3 shows changes in size and volume over time after treatment. After RFA, significant reductions in the mean volume of the ablated nodules were noted at 6- and 12-month follow-up visits (P<0.001). Among the 39 patients, 24 had achieved therapeutic success at the 6-month follow-up and 37 had achieved therapeutic success at the 12-month follow-up. The therapeutic success rates were 61.5% (24/39) and 94.9% (37/39) at the 6- and 12-month follow-up visits, respectively. After the procedures, both symptom and cosmetic scores showed significant decreases at the 6- and 12-month follow-up visits (P<0.001 for both).
During RFA of the nodule margin, almost all patients complained of pain, which was controlled by continuous ALHD instead of lidocaine. All patients tolerated the procedure. Transient voice change was observed in one patient, but the patient recovered spontaneously within 30 minutes of cessation of the RFA. At the time when the patient’s voice change was noticed, additional cold (0°C–4°C) 5% dextrose solution was immediately and continuously injected into the tracheoesophageal groove according to the routine management protocol for suspected nerve damage [21]. No patient experienced a complication requiring hospitalization or a delayed complication during follow-up.
ALHD was technically feasible in all patients included in this study cohort. ALHD provided good pain control without additional lidocaine injections, and venous staining was therefore effectively achieved from the marginal venous ablation, which made near-complete ablation of the index nodule possible, as reflected by the high IAR (90.7%). As a result of this high IAR, the VRR at 12 months was 76.3%±18.9%, and the therapeutic success rate was 94.9% (37/39). There was no major complication requiring hospitalization or delayed complications related to the RFA procedures.
The major role of ALHD is to minimize marginal regrowth by achieving a high IAR. It is well known that the final VRR is related to the size of the index nodule, and larger index nodules require more ablation sessions to achieve sufficient volume reduction [3,5]. In a previous study by Lim et al. [3], the number of treatment sessions required to achieve sufficient volume reduction was higher in cases with an index nodule volume >20 mL, and all regrowth arose from the undertreated peripheral portion of the nodule. Therefore, the marginal venous ablation technique and complete tumor ablation, which are represented by venous staining signs and a high IAR, respectively, are important to prevent marginal recurrence. Sim et al. suggested that an IAR of more than 70% could be used as an indicator of expected therapeutic success [5]. In this study, although the mean initial nodule volume was large (20.5±21.6 mL), the mean IAR was high enough to expect therapeutic success (90.7%±8.3%) and the therapeutic success rate at 12 months was 94.9%.
The further roles of ALHD are pain control and prevention of thermal damage to critical structures around the thyroid gland. There are no sensory nerves inside the thyroid gland, but they are abundant in the thyroid capsule and strap muscle. In terms of pain control during RFA, lidocaine can control pain from the thyroid capsule and ALHD can control strap muscle pain. The pain induced by the RF shows an inverse relationship with distance. Therefore, injecting fluid to maintain a separation of 5 mm or more between the thyroid margin and strap muscle can control muscle pain. Compared with a previous study of RFA of benign thyroid nodules by the thyroid team of the authors’ affiliated institution [22], the pain scores during RFA tended to be lower using the hydrodissection technique (1.0±0.7 vs. 0.8±0.9). Thermal damage to the perithyroidal structures may be induced when applying the marginal venous ablation technique, especially for thyroid nodules located at the periphery of the thyroid gland. Thus, when the index nodule is located close to important neck structures, including the recurrent laryngeal nerve, common carotid artery, trachea, and esophagus, complete ablation of the index nodule achieving the venous staining sign is difficult. However, in this study, a safety margin was achieved using the ALHD technique during the procedure, overcoming the limitations and difficulties of the marginal ablation of index nodules located near important neck structures. ALHD with a continuous injection of cold 5% dextrose solution could easily cover not only the lateral compartment, but also the posterior compartment.
General anesthesia or sedation for pain control is not generally recommended for RFA due to the risk of delayed detection of complications during the ablation, resulting in more serious complications [14,23]. With local anesthesia during the ablation procedure, the physician can check for signs of complications such as voice change, eye movement, and irritated trachea signs. In contrast, under general anesthesia, several cases of complications including trachea injury, skin burn, and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury have been reported with ablation procedures [24-26]. For pain relief during RFA, local anesthesia obtained through injection of lidocaine at the skin puncture site and into the perithyroidal area is recommended by the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology [14,27] and is the method mainly used by physicians. Although systemic lidocaine toxicity is a rare complication, it can be life-threatening, with symptoms of circumoral numbness, dizziness, and nausea following hypotension and bradycardia [28,29]. Lidocaine toxicity is strongly correlated with the total dose and rate of absorption, which depend on the blood supply to the tissue [30,31]; therefore, to prevent and minimize systemic toxicity, there is a limit to the total dose of lidocaine that can be given. The experience gained over the course of the procedures described in this study suggests that an injection of cold 5% dextrose solution with the hydrodissection technique, rather than a further injection of lidocaine, can provide effective pain relief when a patient complains of pain. Therefore, the total amounts of lidocaine used during the procedure were relatively small, although the pain was well-controlled. Furthermore, the patients were able to remain in a comfortable state during the procedure.
ALHD has the following advantages compared to other procedures. First, the needle can be placed in the anterior portion and fixed in place, and the hydrodissection technique can be applied with relatively little movement of the needle. Second, the 5% dextrose solutions injected from the anterior aspect can reach the lateral, posterior, and even medial aspects of the thyroid gland as the amount of injected solution increases. Third, ALHD can be applied using the same needle injection site used for lidocaine. A possible limitation of ALHD is inadvertent injection of 5% dextrose solution into strap muscle or thyroid parenchyma. Therefore, experienced interventional skills and anatomical knowledge are necessary to apply ALHD. Four types of hydrodissection have been suggested [12], and of these, the anterolateral approach has several advantages, as described herein. The posterior approach is usual for treating parathyroid adenomas or recurrent tumors close to the danger triangle. The pre-tracheal approach is useful for treating isthmus masses, and the danger triangle approach is useful for treating nodules at the danger triangle.
This study has several limitations. First, the number of cases of RFA performed with ALHD was small, making it difficult to determine whether this technique should be adopted as standard treatment. Large-sized prospective studies are required to determine a standard treatment strategy for the ALHD technique during RFA. Second, the procedures involving ALHD were performed by an experienced radiologist. An operator with less expertise would require learning time to apply ALHD during RFA. Third, although a mean IAR of more than 90% and a VRR of more than 70% were achieved at the 12-month follow-up, longer-term follow-up results are necessary to evaluate the actual clinical effectiveness of ALHD. Fourth, the complications, side effects, and assessment of pain during the procedure were evaluated symptomatically, on the basis of subjective complaints by the patients, not by objective and quantitative criteria. Fifth, because of the retrospective nature of this study, the exact amount of 5% dextrose solution and lidocaine used was unclear. Future studies with exact records of the amount of 5% dextrose solution and lidocaine used are needed.
In conclusion, this study found that the ALHD technique was technically feasible in all patients and effective for achieving near-complete ablation of the index nodule, resulting in a high IAR. The ALHD technique also had a pain-relieving effect, resulting in low quantities of lidocaine administration during the procedure.
NotesAuthor Contributions Conceptualization: Jeong SY, Baek JH. Data acquisition: Jeong SY, Baek JH, Chung SR, Choi YJ, Chung KW, Kim TY, Lee JH. Data analysis or interpretation: Jeong SY, Baek JH. Drafting of the manuscript: Jeong SY, Baek JH, Chung SR, Chung KW, Kim TY. Critical revision of the manuscript: Jeong SY, Baek JH, Choi YJ, Lee JH. Approval of the final version of the manuscript: all authors. References1. Jeong WK, Baek JH, Rhim H, Kim YS, Kwak MS, Jeong HJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur Radiol 2008;18:1244–1250.
2. Na DG, Lee JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Sung JY, Shin JH, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol 2012;13:117–125.
3. Lim HK, Lee JH, Ha EJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Baek JH. Radiofrequency ablation of benign non-functioning thyroid nodules: 4-year follow-up results for 111 patients. Eur Radiol 2013;23:1044–1049.
4. Sim JS, Baek JH. Long-term outcomes following thermal ablation of benign thyroid nodules as an alternative to surgery: the importance of controlling regrowth. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2019;34:117–123.
5. Sim JS, Baek JH, Cho W. Initial ablation ratio: quantitative value predicting the therapeutic success of thyroid radiofrequency ablation. Thyroid 2018;28:1443–1449.
6. Zhao CK, Xu HX, Lu F, Sun LP, He YP, Guo LH, et al. Factors associated with initial incomplete ablation for benign thyroid nodules after radiofrequency ablation: first results of CEUS evaluation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2017;65:393–405.
7. Wang B, Han ZY, Yu J, Cheng Z, Liu F, Yu XL, et al. Factors related to recurrence of the benign non-functioning thyroid nodules after percutaneous microwave ablation. Int J Hyperthermia 2017;33:459–464.
8. Lee M, Baek JH, Suh CH, Chung SR, Choi YJ, Lee JH, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: a systematic review. Ultrasonography 2021;40:256–264.
9. Park HS, Baek JH, Park AW, Chung SR, Choi YJ, Lee JH. Thyroid radiofrequency ablation: updates on innovative devices and techniques. Korean J Radiol 2017;18:615–623.
10. Levit E, Bruners P, Gunther RW, Mahnken AH. Bile aspiration and hydrodissection to prevent complications in hepatic RFA close to the gallbladder. Acta Radiol 2012;53:1045–1048.
11. Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Brace CL, Winter TC 3rd, Fine JP, Lee FT Jr. Unintended thermal injuries from radiofrequency ablation: protection with 5% dextrose in water. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006;186:S249–S254.
12. Chung SR, Baek JH, Choi YJ, Lee JH. Thermal ablation for the management of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in the era of active surveillance and hemithyroidectomy. Curr Oncol Rep 2022;24:1045–1052.
13. Ha EJ, Chung SR, Na DG, Ahn HS, Chung J, Lee JY, et al. 2021 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol 2021;22:2094–2123.
14. Kim JH, Baek JH, Lim HK, Ahn HS, Baek SM, Choi YJ, et al. 2017 Thyroid radiofrequency ablation guideline: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol 2018;19:632–655.
15. Kim YJ, Baek JH, Ha EJ, Lim HK, Lee JH, Sung JY, et al. Cystic versus predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: efficacy of ethanol ablation and analysis of related factors. Eur Radiol 2012;22:1573–1578.
16. Sung JY, Baek JH, Kim KS, Lee D, Yoo H, Kim JK, et al. Single-session treatment of benign cystic thyroid nodules with ethanol versus radiofrequency ablation: a prospective randomized study. Radiology 2013;269:293–300.
17. Burke DR, Lewis CA, Cardella JF, Citron SJ, Drooz AT, Haskal ZJ, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and biliary drainage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2003;14:S243–S246.
18. Kim HJ, Baek JH, Cho W, Sim JS. Long-term follow-up of the radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: the value of additional treatment. Ultrasonography 2022;41:661–669.
19. Jung SL, Baek JH, Lee JH, Shong YK, Sung JY, Kim KS, et al. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation for benign thyroid nodules: a prospective multicenter study. Korean J Radiol 2018;19:167–174.
20. Mauri G, Pacella CM, Papini E, Solbiati L, Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, et al. Image-guided thyroid ablation: proposal for standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Thyroid 2019;29:611–618.
21. Lee MK, Baek JH, Chung SR, Choi YJ, Lee YM, Kim TY, et al. Effectiveness of injecting cold 5% dextrose into patients with nerve damage symptoms during thyroid radiofrequency ablation. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2020;35:407–415.
22. Jeong SY, Ha EJ, Baek JH, Kim TY, Lee YM, Lee JH, et al. Assessment of thyroid-specific quality of life in patients with benign symptomatic thyroid nodules treated with radiofrequency or ethanol ablation: a prospective multicenter study. Ultrasonography 2022;41:204–211.
23. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Che Y, Chou YH, Fukunari N, Kim JH, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: recommendations from the Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Task Force. Ultrasonography 2021;40:75–82.
24. Ahmed M, Lobo SM, Weinstein J, Kruskal JB, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, et al. Improved coagulation with saline solution pretreatment during radiofrequency tumor ablation in a canine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002;13:717–724.
25. Di Rienzo G, Surrente C, Lopez C, Quercia R. Tracheal laceration after laser ablation of nodular goitre. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2012;14:115–116.
26. van Baardewijk LJ, Plaisier ML, van den Broek FJ, van Poppel P, Kurban S, Kruimer JW. Tracheal necrosis following radiofrequency ablation of a benign thyroid nodule. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2021;44:170–171.
27. Shin JH, Baek JH, Chung J, Ha EJ, Kim JH, Lee YH, et al. Ultrasonography diagnosis and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: revised Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol 2016;17:370–395.
28. Nguyen VB, Nguyen VV, Tuyen LP, Le CV. Lidocaine-induced systemic toxicity complicating radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodule procedure: a case report and review of literature. Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e04910.
29. Kim C, Lee JH, Choi YJ, Kim WB, Sung TY, Baek JH. Complications encountered in ultrasonography-guided radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers. Eur Radiol 2017;27:3128–3137.
30. Neal JM, Woodward CM, Harrison TK. The American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine checklist for managing local anesthetic systemic toxicity: 2017 version. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2018;43:150–153.
The 6-inch-long needle with a three-way stopcock used in the anterolateral hydrodissection technique.Both the 1% lidocaine syringe (blue) and the cold (0°C-4°C) 5% dextrose solution syringe (green) are connected to one 6-inch-long needle, and a single skin puncture site is used for both local anesthesia and anterolateral hydrodissection.
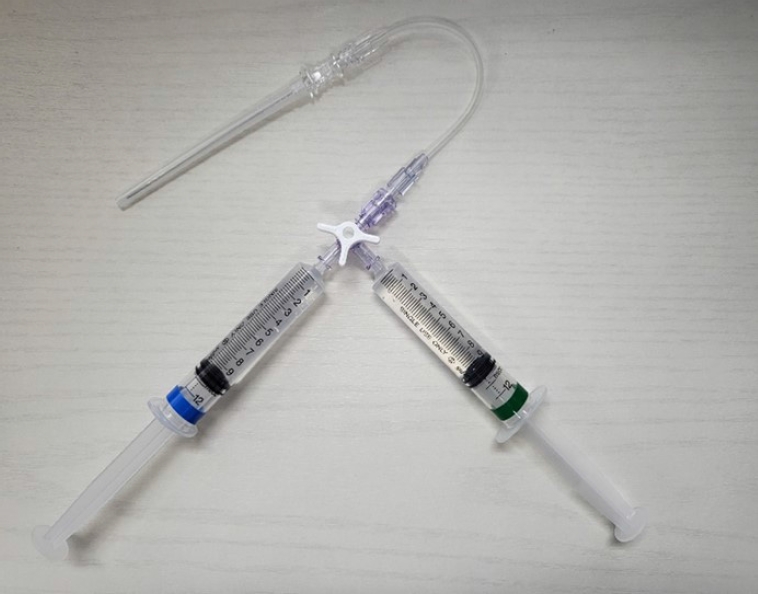 Fig. 2.The overall procedure for anterolateral hydrodissection (HD) with radiofrequency ablation.The target nodule is divided into three portions and ablated in the order 1, 2, and 3, as shown in the illustration. First, the anteromedial portion (1) near the isthmus is targeted. Second, the central portion of the nodule (2) is targeted. Third, the peripheral portion of the nodule (3), which is relatively close to the critical perithyroidal structures, is targeted. All target areas are ablated using strict HD.
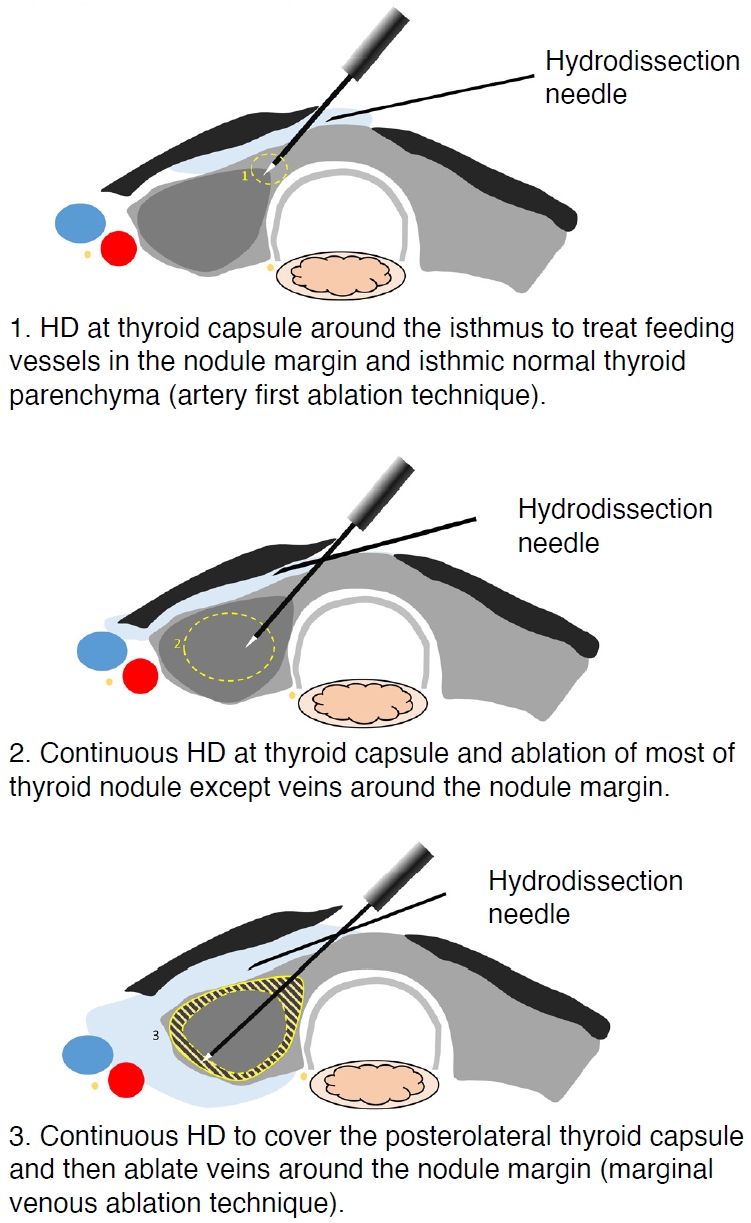 Fig. 3.Anterolateral hydrodissection covering lateral compartment and posterior compartment.Adjacent structures were monitored carefully, and anterolateral hydrodissection with cold 5% dextrose solution was performed to secure sufficient safety margins from critical structures. Continuous injection of cold 5% dextrose solution could easily cover not only the lateral compartment, but also the posterior compartment (arrows).
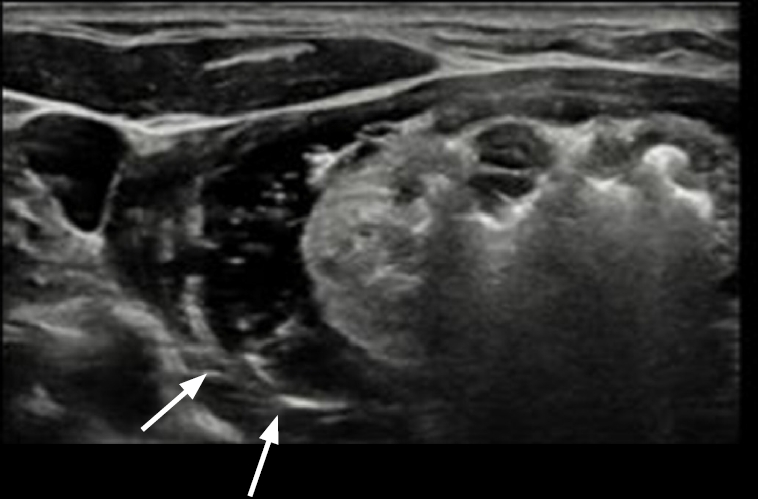 Fig. 4.Table 1.Baseline characteristics of the patients and nodules Table 2.Treatment characteristics in the 41 RFA sessions Table 3.Ultrasound features, cosmetic scores, and symptom scores before and after the procedures
|



 Print
Print facebook
facebook twitter
twitter Linkedin
Linkedin google+
google+
 Download Citation
Download Citation PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI